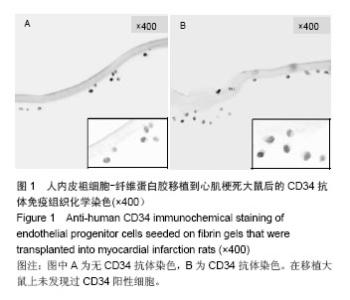
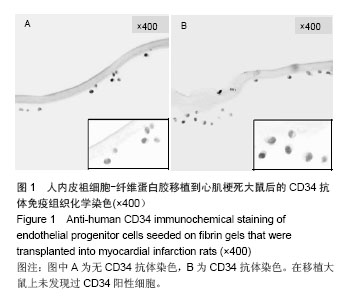
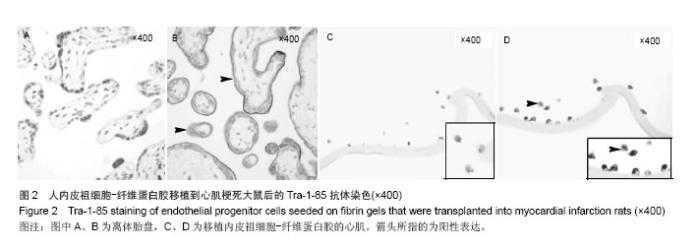
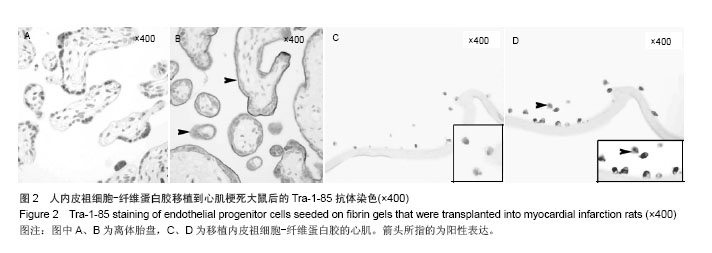
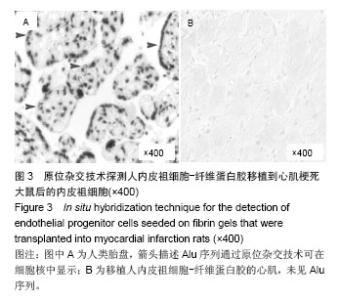
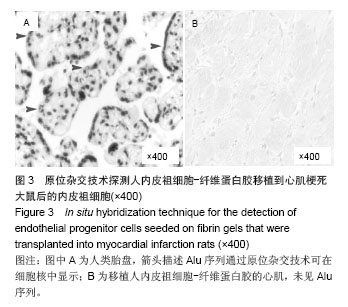
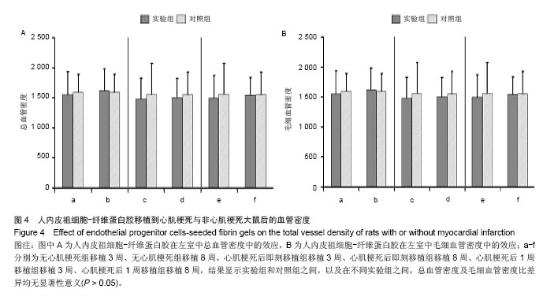
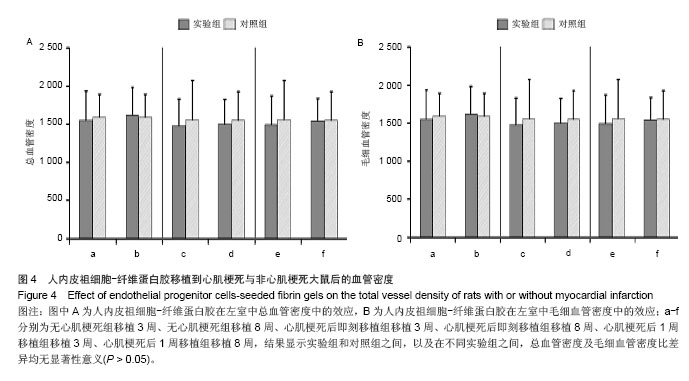
| [1]吕树铮.冠心病介入治疗新进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2007,9(3):145-148.
[2]张倞,王永武.心肌组织工程研究进展[J].心脏杂志,2007,19(2): 230-231.
[3]Chachques JC,Trainini JC,Lago N,et al.Myocardial assistance by grafting a new bioartificial upgraded myocardium (MAGNUM clinical trial):one year follow-up.Cell Transplant. 2007;16(9):927-934.
[4]Yang CF,Chou KY,Weng ZC,et al.Cardiac myocyte progenitors from adult hearts for myocardial regenerative therapy.J Chin Med Assoc.2008;71(2):79-85.
[5]王亚东,袁南荣,刘超,等.自体组织工程化角膜上皮修复角膜缘缺陷症[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(46):65-68.
[6]Kobayshi T,Ochi M,Yanada S,et al.A novel cell delivery system using magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells and an external magnetic device for clinical cartilage repair. Arthroscopy.2008;24(1):69-76.
[7]张晓勇,黎键.心肌梗死的干细胞治疗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(11):2197-2200.
[8]DowJ,Simkhovich BZ,Kedes L,et al.Washout of transplanted cells from the heart:A protenial new hurdle for cell transplantation therapy.Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67(2):301-307.
[9]黄清.冠心病急性心肌梗死与左心室重构及心脏功能[J].中华现代影像学杂志,2005,2(4):374-375.
[10]孙雪,奚廷斐.生物材料和再生医学的进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(2):189-193.
[11]刘盛辉,郎美东.新一代生物医用材料[J].高分子通报,2005,19(6): 113-117.
[12]Almany L,Seliktar D.Biosynthetic hydrogel scaffolds made from fibrinogen and polyethylene glcol for 3D cell cultures. Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2467-2477.
[13]段志军,张振方,童昕.组织工程支架材料三维多孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶的制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(48): 9762-9764.
[14]Lee KY,Peters MC,Anderson KW,et al.Controlled growth factor release from synthetic extracellular matrices. Nature. 2000;408(6815):998-1000.
[15]侯天勇,许建忠.藻酸盐在构建组织工程骨运用研究中的进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2006,22(12):949-951.
[16]Partt AB,Weber FE,Schmoekel HG,et al.Synthetic extracellular matrices for in situ tissue engineering.Biotechnol Bioeng.2004;86(1):27-26.
[17]胡晓熙,徐祖顺,易昌凤.PEG类大分子引发剂在聚合反应中的运用[J].材料导报:网络版,2007,2(1):59-62.
[18]潘海涛,郑启新,郭晓东.骨髓基质干细胞与聚丙交酯/乙交酯/天冬氨酸/聚乙二醇体外复合培养的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(1):65-69.
[19]Zimmermann WH,Melnychenko I,Eschenhagen T.Engineered heart tissue for regeneration of diseased hearts. Biomaterials. 2004;25(9):1639-1647.
[20]Rafii S,Lyden D.Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med.2006;9:702-712.
[21]Christman KL,Fok HH,Sivers RE,et al Fibrin glue and srkeletal myoblast in a fibrin scaffold preserve cardiac function after myocardial infarction.tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4): 403-409.
[22]Christman KL,Vardanian AJ,Fang Q,et al.Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival,reduces infarct expansion,and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium.J Am Coll Cardiol.2004;4(4):654-660.
[23]Ryu IK,Kim IK,Cho SW,et al.Implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells using injectable fibrin matrix enhances neovascularization in infracted myocardium. Biomaterrials. 2005;26(3):319-326.
[24]李冰一,蔺嫦燕,曹谊林.组织工程支架材料的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2007,11(3):241-246
[25]Zisch AH,Schenk U,Schense JC,et al.Covalently conjugated VEGF-fibrin matrices for endothelialization.J Control Release. 2001;72(13):101-113.
[26]Ye J,Yang L,Sethi R,et al.A new technique of coronary artery ligation:experimental myocardial infarction in rats in vivo with reduced mortality. Mol Cell Biochem. 1997;176 (1-2):227-233.
[27]Ertl G,Frantz S. Wound model of myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol heart Circ Physiol.2005;288(3):H981-H983
[28]Sullivan PG,Thompson M,Scheff SW.Continuous infusion of cyclosporin A postinjury significantly ameliorates cortical damage following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2000; 161(2):631-637.
[29]Litwin S,Katz S,Morgan J,et al.Serial echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular geometry and function after large myocardial infarction in the rat. Circulation. 1994;89: 345-354.
[30]Moisés VA,Ferreira RL,Nozawa E,et al.Structural and functional characteristics of rat hearts with and without myocardial infarct. Initial experience with Doppler echocardiography. Arq Bras Cardiol.2000;75(2):125-136.
[31]Asahara T,Murohara T,Sullivan A,et al.Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997; 275(5302):964-967.
[32]Kalka C,Masuda H,Takahashi T,et al.Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(7): 3422-3427.
[33]Condorelli G,Borello U,De Angelis L,et al.Cardiomyocytes induce endothelial cells to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle: implications for myocardium regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2001;98:10733-10738.
[34]Urbich C,Heeschen C,Aicher A,et al.Relevance of monocytic features for neovascularization capacity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Circulation.2003;108:2511-2516.
[35]Gulati R,Jevremovic D,Peterson TE,et al.Diverse origin and function of cells with endothelial phenotype obtained from adult human blood.Circ Res.2003;93:1023-1025.
[36]Iwaguro H,Yamaguchi J,Kalka C, et al.Endothelial progenitor cell vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer for vascular regeneration. Circulation.2002; 105:732-738. |